Protectli Vault FW6 series
This page describes how to run coreboot on the Protectli FW6.
Stock firmware
The stock firmware contains only the firmware descriptor, BIOS and Management Engine. The EC firmware is not present on the SPI chip.
Using ifdtool, a full layout can be obtained along with the ME and FD flash regions.
Required proprietary blobs
To build a minimal working coreboot image some blobs are required (assuming only the BIOS region is being modified).
Binary file |
Apply |
Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
FSP-M, FSP-S |
Intel Firmware Support Package |
Required |
microcode |
CPU microcode |
Required |
vgabios |
VGA Option ROM |
Optional |
FSP-M and FSP-S are obtained after splitting the Kaby Lake FSP binary (done
automatically by the coreboot build system and included into the image) from
the 3rdparty/fsp submodule.
Microcode updates are automatically included into the coreboot image by build
system from the 3rdparty/intel-microcode submodule.
VGA Option ROM is not required to boot, but if one needs graphics in pre-OS stage, it should be included (if not using libgfxinit).
Flashing coreboot
Internal programming
The main SPI flash can be accessed using flashrom. The first version supporting the chipset is flashrom v1.1. Firmware an be easily flashed with internal programmer (either BIOS region or full image).
The stock firmware can be dumped using flashrom or downloaded from Protectli’s official website.
External programming
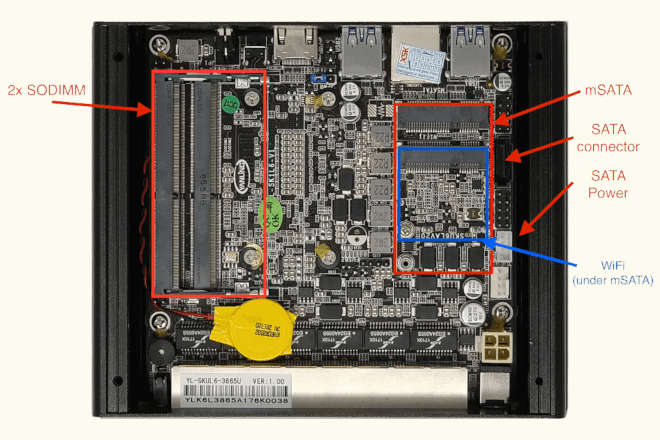
The system has an internal flash chip which is a 8 MiB soldered SOIC-8 chip. This chip is located on the bottom side of the case (the radiator side). One has to remove all screws (in order): 4 top cover screws, 4 side cover screws (one side is enough), 4 mainboard screws, 4 CPU screws (under DIMMs). Lift up the mainboard and turn around it. The flash chip is near the SoC on the DIMM slots side. Desolder and reprogram the chip, or use a clip (or solder the wires) to program the chip. Specifically, it’s a Macronix MX25L6406E (3.3V) -datasheet, while on some other boards it’s a Macronix MX25L6436F.
At least on some revisions of the motherboard, it’s not possible to reprogram the chip with a clip, while the board is powered off, because there’s no diode to prevent backfeeding power to other components on the board.
Known issues
After flashing with external programmer it is always required to reset RTC with jumper or disconnect coin cell temporarily. Only then the platform will boot after flashing.
FW6A does not always work reliably with all DIMMs. Linux happens to hang or gives many panics. This issue was present also with vendor BIOS.
Sometimes FSPMemoryInit return errors or hangs (especially with 2 DIMMs connected). A workaround is to power cycle the board (even a few times) or temporarily disconnect DIMM when platform is powered off.
When using libgfxinit and SeaBIOS bootsplash, the red color is dim.
Untested
Not all mainboard’s peripherals and functions were tested because of lack of the cables or not being populated on the board case.
Internal USB 2.0 headers
Working
USB 3.0 front ports (SeaBIOS and Linux)
6 Ethernet ports
HDMI port with libgfxinit and VGA Option ROM
flashrom
PCIe WiFi
SATA and mSATA
Super I/O serial port 0 (RS232 via front RJ45 connector)
SMBus (reading SPD from DIMMs)
Initialization with KBL FSP 2.0 (with MemoryInit issues)
SeaBIOS payload (version rel-1.12.1)
Mini PCIe debug card connected to mSATA (mSATA slot has LPC signals routed)
Reset switch
Booting Debian, Ubuntu, FreeBSD, Proxmox
PCIe passthrough for NICs and iGPU
Boot with cleaned ME
Technology
There are 5 variants of FW6 boards: FW6A, FW6B, FW6C, FW6D and FW6E. They differ in used SoC.
There are two revisions of the motherboard, hereby called Old Revision (using IT8772E Super I/O chip), and New Revision (using IT8613E Super I/O chip). Besides the different Super I/O chip, they also differ in component placement, and available internal motherboard headers. The Old Revision motherboards are marked with silkscreen “YL-SK1L6-V1”, while the New Revision motherboards are marked with silkscreen “KBR6LAV20”.
WARNING: The current code base only supports the Old Revision motherboards.
To compare the two motherboard revisions one may compare the New Revision FW6A Datasheet to the Old Revision FW6 Series Hardware Overview.
The FW6A/FW6B/FW6C variants are known to have been produced with both motherboard revisions.
The FW6D/FW6E variants are only known to exist with the new motherboard revision.
FW6A:
CPU |
Intel Celeron 3865U |
PCH |
Kaby Lake U w/ iHDCP2.2 Base |
Super I/O, EC |
Old revision: ITE IT8772E, New rev.: ITE IT8613E |
Coprocessor |
Intel Management Engine |
Support |
Currently only the Old Revision is supported |
FW6B:
CPU |
Intel Core i3-7100U |
PCH |
Kaby Lake U w/ iHDCP2.2 Premium |
Super I/O, EC |
Old revision: ITE IT8772E, New rev.: ITE IT8613E |
Coprocessor |
Intel Management Engine |
Support |
Currently only the Old Revision is supported |
FW6C:
CPU |
Intel Core i5-7200U |
PCH |
Kaby Lake U w/ iHDCP2.2 Premium |
Super I/O, EC |
Old revision: ITE IT8772E, New rev.: ITE IT8613E |
Coprocessor |
Intel Management Engine |
Support |
Currently only the Old Revision is supported |
FW6D:
CPU |
Intel Core i5-8250U |
PCH |
Kaby Lake U w/ iHDCP2.2 Premium |
Super I/O, EC |
ITE IT8613E |
Coprocessor |
Intel Management Engine |
Support |
Currently not supported |
FW6E:
CPU |
Intel Core i7-8550U |
PCH |
Kaby Lake U w/ iHDCP2.2 Premium |
Super I/O, EC |
ITE IT8613E |
Coprocessor |
Intel Management Engine |
Support |
Currently not supported |
Other compatible boards
As Protectli licenses and uses Yanling appliances with no modifications to the actual hardware, any compatible Yanling appliances would work. Specifically, look for hardware with the same CPU, NIC, and Super I/O chip and coreboot should be able to compile and boot with no modifications required.